Autoscaling
Why Autoscaling is Important
In Azure Virtual Desktop, virtual machines incur usage costs even when there are no connected desktop sessions. Autoscaling can be essential to ensure unused machines do not increase costs. That said, even when machines are powered off (“deallocated”) through autoscaling, storage costs persist. Hydra has solutions for both of these scenarios.
Configuring Auto-Scale: Pooled Host Pools
From the main Dashboard:
Find the host pool where auto-scaling should be configured, and open its Configuration.
Open the Autoscale & Autoshutdown pane of the Host Pool configuration.
In the Autoscale configuration section, fill in the following details:
Enabled: Determines whether to apply the configured Autoscale & Autoshutdown settings.
Use Power-On-Connect: Dictates whether Microsoft Power-On-Connect is enabled for the host pool; host pools will have zero session hosts until the first user connection, at which point the Session Host will dynamically be deployed, as opposed to static Schedules.
Session hosts running 24/7: Determines the number of session hosts running 24/7; at least one session host is required to allow user logins (unless using Power-On-Connect).
Default LoadBalancer Type: Dictates the load-balancer type for the host pool—either Depth-first (user sessions will be brokered until a Max Session Limit is met) or Breadth-first (user sessions will be brokered across all available Session Hosts).
Depth-first is recommended
Min. number of available sessions: Determines the capacity for new sessions; e.g., a Min. number of available sessions value of 5 means there will always be enough session hosts to support 5 sessions; a value of 0 means there are no session hosts.
Min. number of hosts without sessions: Determines how many session hosts should be available without any user sessions; e.g., a Min. number of hosts without sessions value of 0 means there are no session hosts.
Dynamically rollout new session: Hosts up to a max number of hosts in the pool determines the maximum number of allowed session hosts in the host pool, when the New Session Host Rollout configuration is set.
Note: Power-On-Connect cannot trigger the creation of new session hosts
Concurrent starts/rollouts of session: Hosts at the same time limit the number of parallel starts (creation) of session hosts. The Concurrent starts/rollouts of session hosts at the same time value should be higher in larger environments for quicker rollouts.

Scheduling Capacity
Schedules can be used to define a minimum number of session hosts for a specific time range to handle login storms. For example, a default of five sessions hosts between 6:00 am and 8:00 am on weekdays.
From the Autoscale & Autoshutdown page of the host pool where Schedules are desired:
Find the Schedules table, and click Add to create a new Schedule
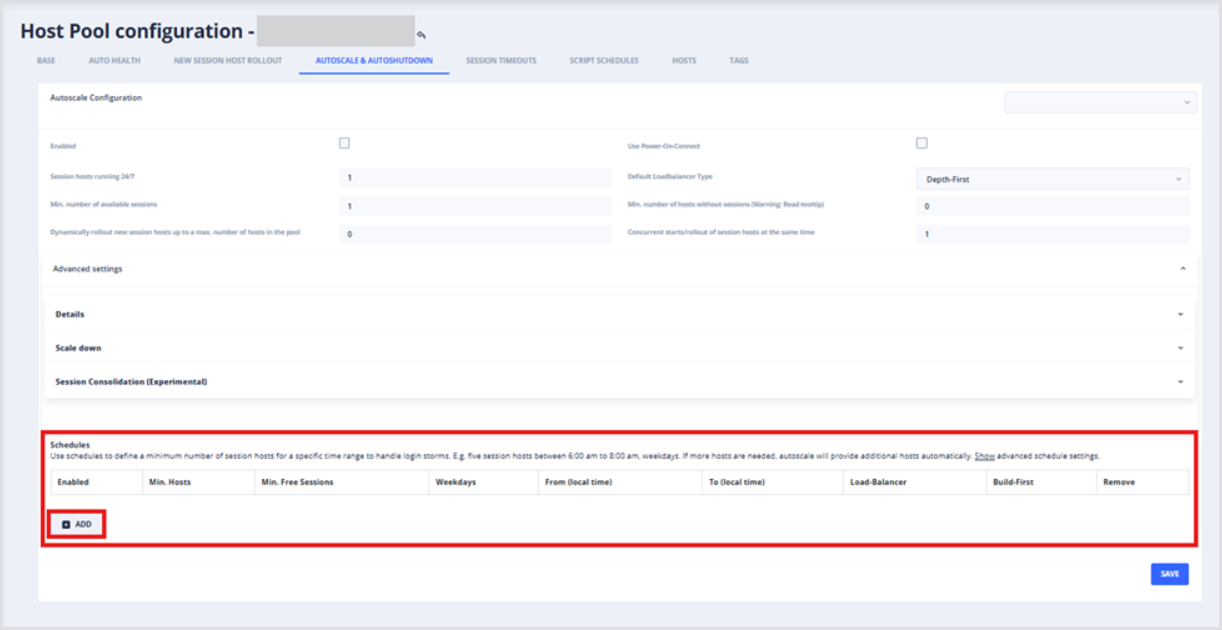
A new Schedule item will appear in the Schedules table with default settings configured:

Now that the Schedule item is created, configure the following settings:
Min. Hosts: Determines the minimum number of session hosts running in the scheduled timeframe; Hydra will start and/or create additional hosts as needed.
Min. Free Sessions (optionally): Determines the minimum number of available sessions during the scheduled timeframe.
Weekdays selected: Activates the Schedule.
From (local time): Determines the starting time on selected Weekdays when the Schedule is active.
Note: Configure the Host Pool Time-Zone on the Base tab.
To (local time): Determines the ending time on selected Weekdays when the Schedule will be deactivated.
Note: Configure the Host Pool Time-Zone on the Base tab.
Load-Balancer: Configures the load-balancing behavior of the host pool; this can be different than the default Load-Balancer Type configured in the Configure Auto-scaling section above. For example, a schedule might use Breadth-first and Min. Hosts settings to spread logons across hosts, dramatically improving logon times during logon storms.
Build-First: Determines whether to temporarily deploy a new session host to reach the minimum level of hosts for this time frame, as opposed to starting existing ones. When no longer needed, they are deleted as opposed to deallocated, saving costs for compute and storage.
Scheduling Capacity: Best Practices
Based on experience and testing, there are best practices for leveraging schedules:
Create a New Session Host Rollout configuration and test it.
Enable Use Power-On-Connect and bring down the Session Hosts Running 24/7 value to 0.
Create permanent session hosts that are available and will be started during user connections; starting session hosts is faster than creating them.
Use a schedule to provide temporarily created Session Hosts during the busiest timeframes; temporary hosts will be deleted if no longer needed (as opposed to only deallocating them, which saves additional costs on disks).
Configure Session Timeouts to log off disconnected sessions, allowing for further automatic deallocation (or deletion of temporary hosts) of deployed session hosts
Below, an example configuration is shown to achieve the best practices:
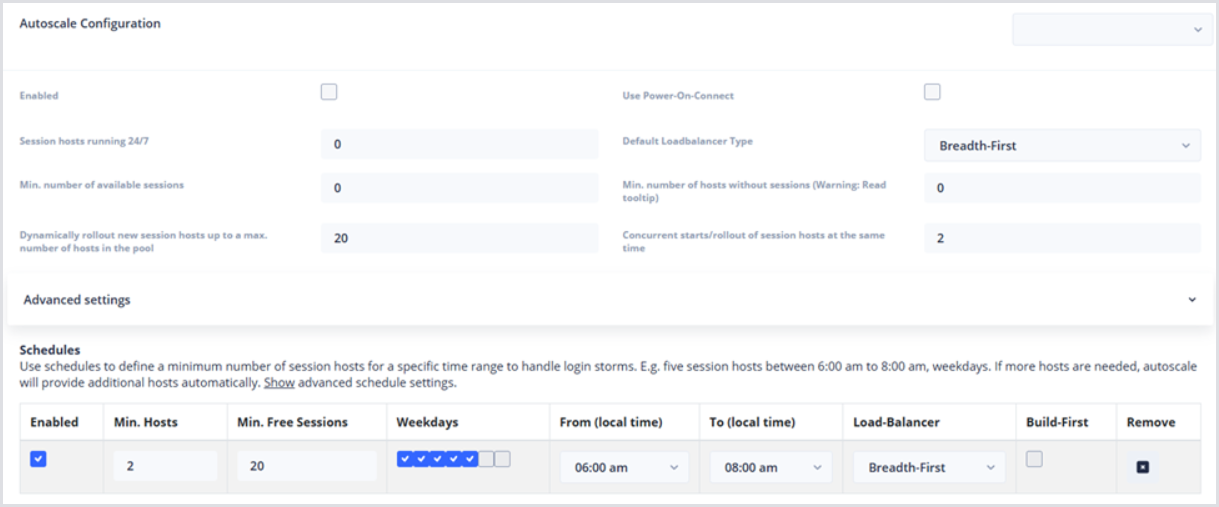
Advanced Settings
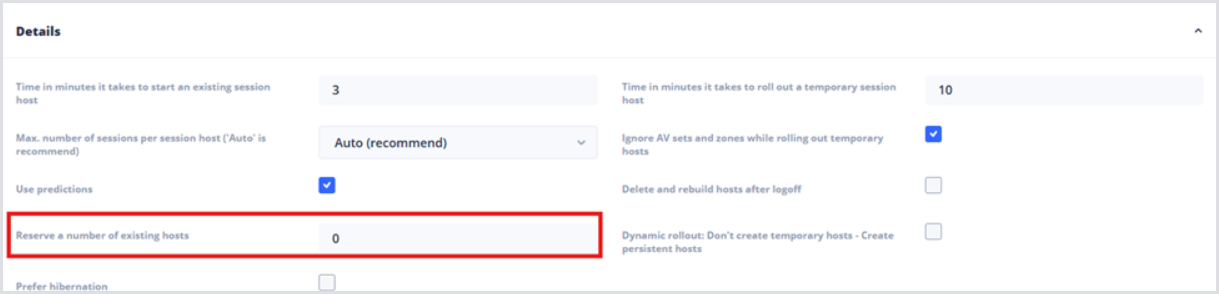
Reserving a Number of Existing Hosts
In addition to the default usage of the Build-First setting, one of the Advanced Settings worth mentioning here is the ability to reserve existing hosts as part of your Autoscaling logic.
By default, Hydra will attempt to provision additional Session Hosts to handle increased user demand. However, tasks such as domain joins or application installs may delay the process, resulting in end-users who have to wait for their session host to deploy. Instead of an error message indicating there are no available session hosts, the user gets notified that a session host is being powered on for them.
Automatic Disk-Swap will not function in this scenario. In the backend, the user is actually sending the power-on command to the session host. Hydra is not involved in this operation; thus, it cannot perform the disk swap.
Power-on-Connect must be used in these scenarios.
From your Host Pool configuration page, open the Advanced Settings, and then open the Details drop-down.
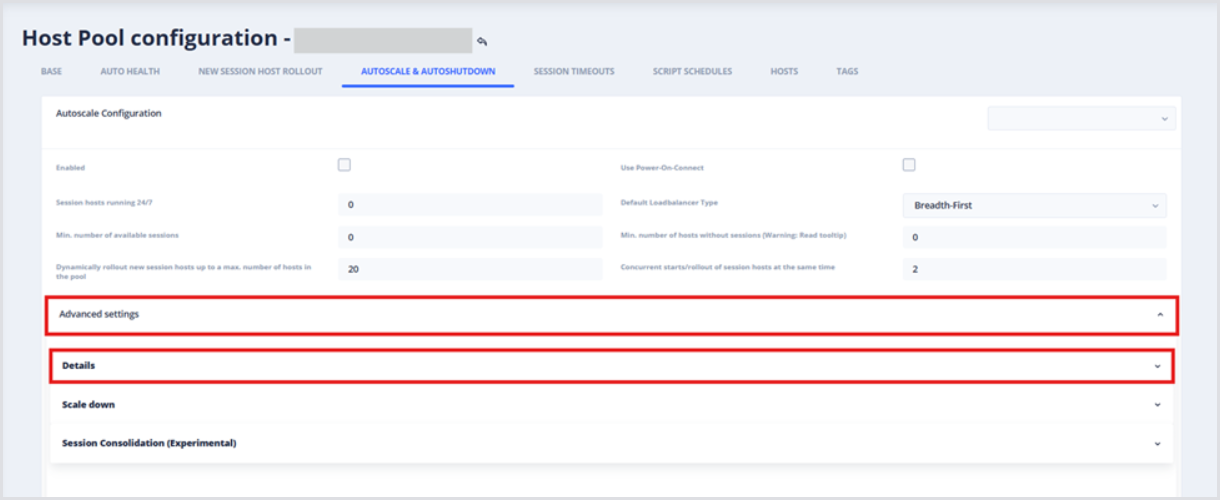
Find the Reserve a number of existing hosts field and input the desired value.
Session Consolidation
The Session Consolidation section provides a non-disruptive way to minimize the number of hosts off-hours to support your users. A few items to note about Session Consolidation:
Session Consolidation temporarily sets the Load Balancer to Depth First. This ensures that new sessions don't get brokered to hosts that Hydra is trying to consolidate.
Session Consolidation does not force users to log off - it only messages them.
Session Consolidation triggers whenever the Autoscaling Base Configuration is in use. That is, whenever a defined autoscaling schedule is not active.
The following options are available:
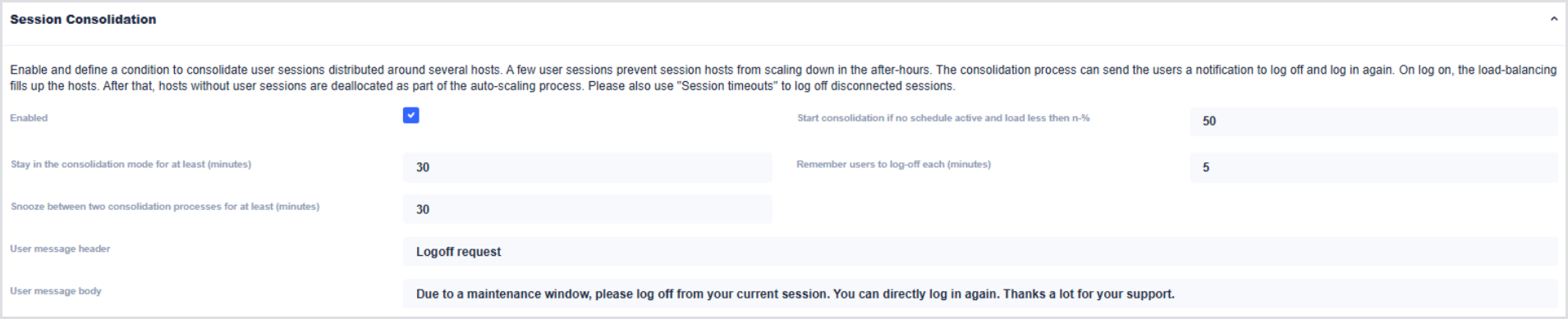
Stay in the consolidation mode for at least (minutes): Defines the amount of time the pool should remain in Depth First and continue messaging users
Snooze between two consolidation processes for at least (minutes): Defines the amount of time to wait until the next consolidation kicks off after the time above has ended.
Start consolidation if no schedule active and load less than n-%: Defines the pool's load percentage based on the host capacity configuration to determine if Session Consolidation is necessary and should proceed. Once both the load is less than this percentage and an autoscaling schedule is not active.
Remember users to log-off each (minutes): Defines how often we should message users while the consolidation process is active.
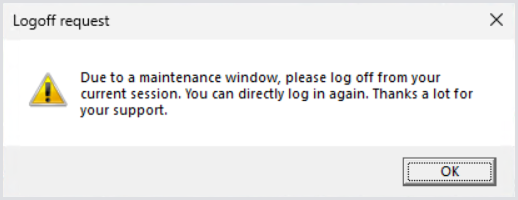
User message header and user message body: Defines the messaging parameters sent to the user. For example, the default messaging will look as follows:
Configuring Auto-Scale: Personal Host Pools
Personal, or persistent host pools contain assigned session hosts for named users. Because of the inherent differences between Personal and Pooled host pools, the auto-scaling configuration is different.
It is recommended to use Power-On-Connect for Personal Pools, such that users can start their sessions as needed, and let autoscaling schedules handle power management.
From the main Dashboard:
Find the host pool where auto-scaling should be configured, and open its Configuration.

From the Host Pool configuration page, open the Autoscale & Auto shutdown setting:
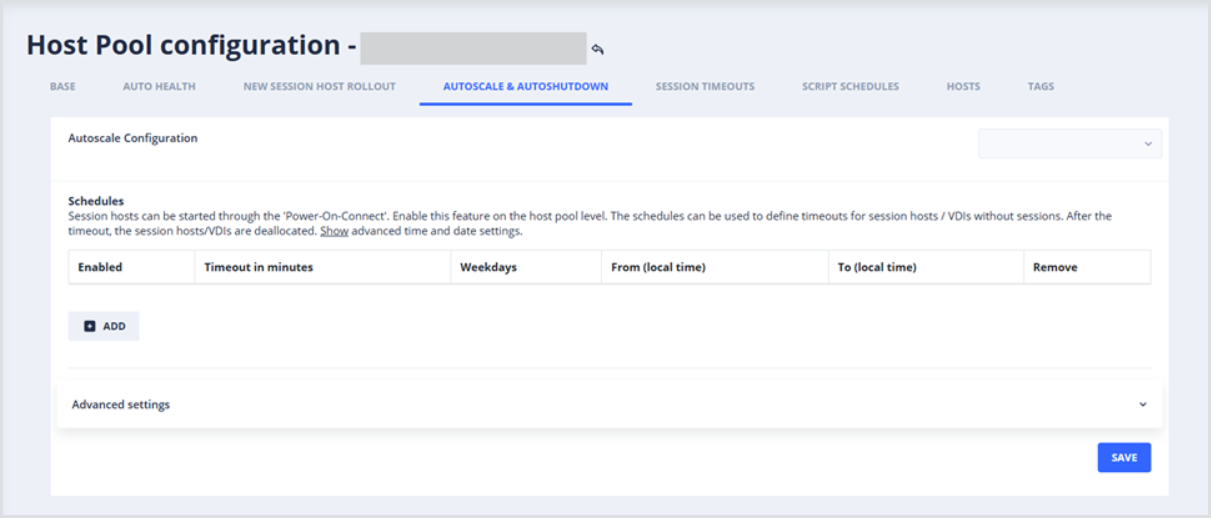
Click Add to create a new Autoscale configuration. Now that the Schedule item is created, configure the following settings:
Timeout in minutes: Determines how long to wait before deallocating an unused session host; i.e., after the user logs off
Weekdays selected: Activates the Schedule.
From (local time): Determines the starting time on selected Weekdays when the Schedule is active.
Note: Configure the Host Pool Time-Zone on the Base tab.
To (local time): Determines the ending time on selected Weekdays when the Schedule will be deactivated.
Note: Configure the Host Pool Time-Zone on the Base tab.
Below is an example host pool that is configured to shut down unused session hosts after 20 minutes, which is active every hour, of every day of the week.
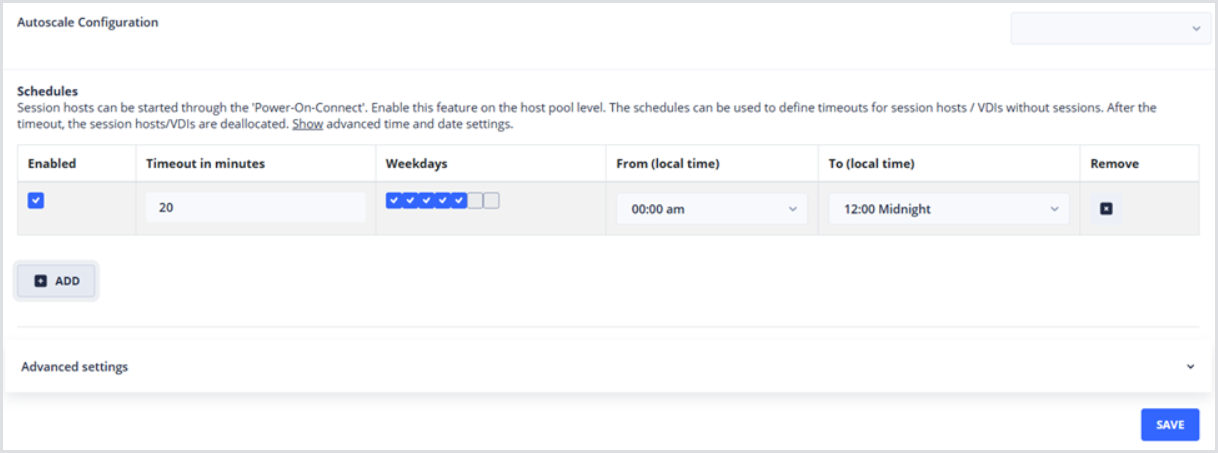
The Timeout in minutes setting will deallocate unused session hosts, where unused refers to a session host with no sessions. Disconnected sessions, while inactive, do not meet this criterion. Use the Session Timeouts setting at the Host Pool level to automatically log off disconnected users after a certain threshold, at which point the Timeout in minutes setting can deallocate them.
.png)