Configuring Single Sign-On (SSO)
Overview
Single sign-on (SSO) allows users to sign in once and access Login Enterprise without repeated authentication prompts. Authentication is handled by Microsoft Entra ID, which verifies user identities and manages sign-in.
Using SSO helps streamline the sign-in experience and align authentication with organizational security policies. By using Microsoft Entra ID, organizations can enforce controls such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), reduce password management overhead, and improve overall security.
How SSO works
In Login Enterprise, authentication and authorization are handled separately:
Authentication is performed by Microsoft Entra ID through single sign-on (SSO).
Authorization is handled by LDAP.
After a user signs in through Microsoft Entra ID, Login Enterprise queries LDAP to determine the user’s group membership, such as whether the user belongs to the right AD groups, to decide what access they should have. For this reason, LDAP must be configured even when SSO is enabled.
Prerequisites
Before configuring single sign-on (SSO), ensure that the following requirements are met:
An LDAP configuration is in place. For more information, see Configuring Authentication.
LDAP credentials are available.
These credentials are optional when saving the LDAP configuration without SSO.
These credentials are required when SSO is enabled to query user and group information for role assignment.
A Microsoft Entra tenant is available.
An enterprise application is created in Microsoft Entra.
Configuring SSO in Microsoft Entra
To use single sign-on (SSO), you must enable SSO for an enterprise application in your Microsoft Entra tenant. This application is used to authenticate users who sign in to Login Enterprise.
For general guidance on configuring single sign-on in Microsoft Entra ID, see the Microsoft documentation.
Configuration options such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), conditional access, and user assignment are managed in Microsoft Entra and are outside the scope of this documentation.
Configuring SSO in Login Enterprise
Sign in to Login Enterprise using the local admin account.
In the Login Enterprise sidebar, navigate to Access Control > SSO configuration.
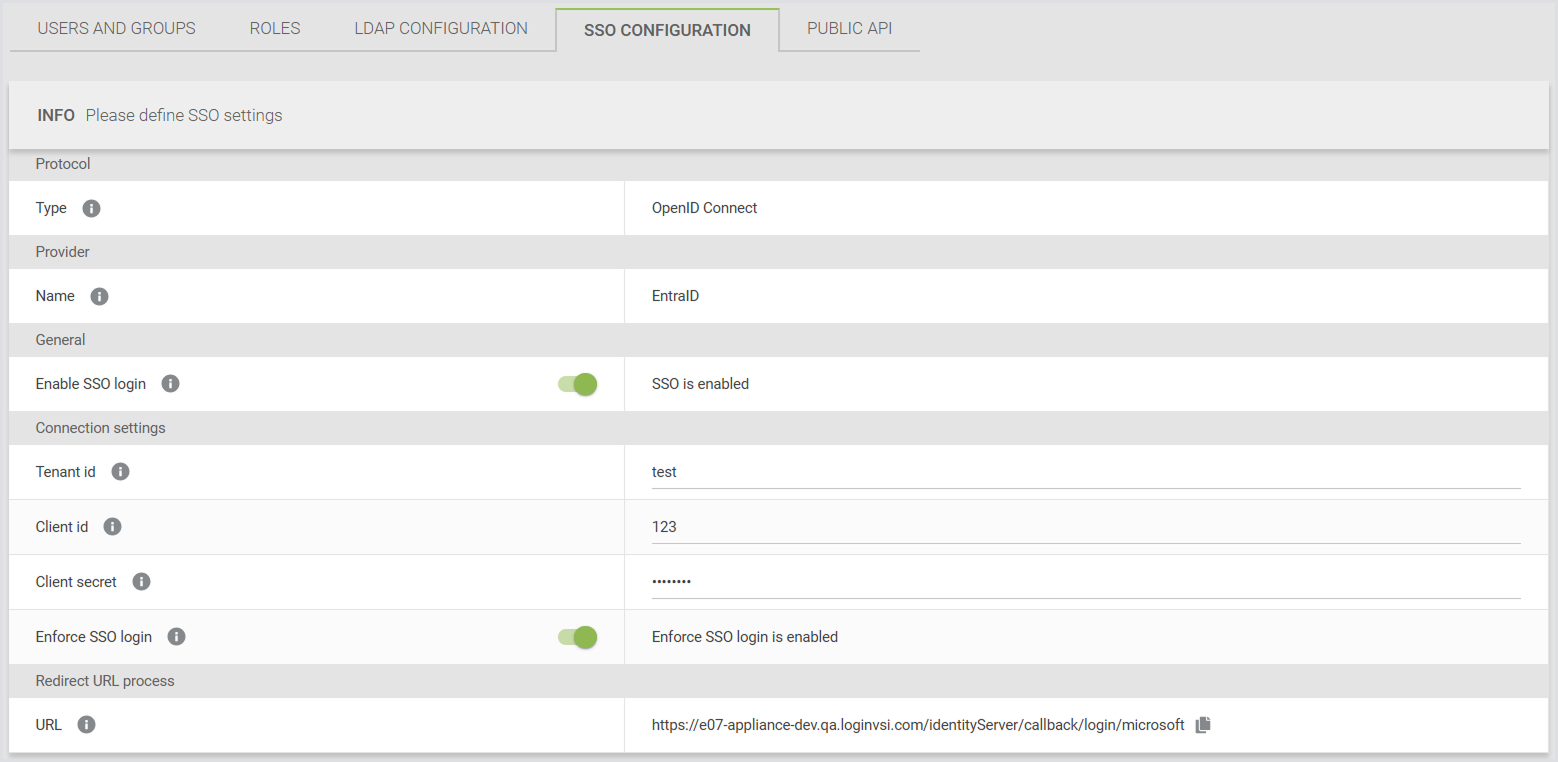
Configure the following fields:
Field | Description |
|---|---|
Type | The protocol used for SSO. Only OpenID Connect is supported. |
Name | The identity provider used for SSO. Only Microsoft Entra ID is supported. |
Enable SSO login | When disabled, the SSO login option isn’t available on the login page. |
Tenant ID | The Microsoft Entra tenant (directory) ID to authenticate users. This value is a GUID and determines which directory is used for sign-in. |
Client ID | The application (client) ID of the Microsoft Entra app for SSO. |
Client Secret | The client secret for the Microsoft Entra app registration, used to authenticate the application. |
Enforce SSO login | When enabled, users can sign in only with SSO or the local admin account. Enforcing SSO login prevents users from bypassing organizational sign-in policies by using local credentials. |
Redirect URL | The Login Enterprise-generated URL that Microsoft Entra uses to redirect users after successful sign-in. It cannot be edited in the Login Enterprise, but can be modified when pasting it into the Microsoft configuration. You can add multiple URLs in Microsoft if needed for multiple domains. |
Save the configuration.
Testing the Configuration
To verify that SSO is configured correctly:
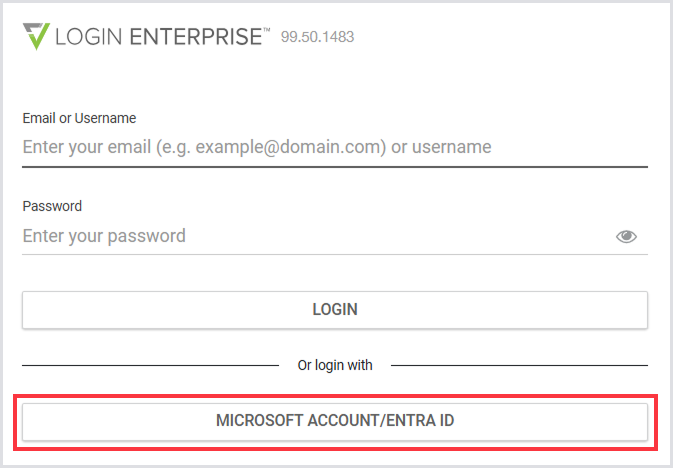
Sign out of Login Enterprise.
Select Microsoft Account/Entra ID on the login page.
Optionally, confirm that you’re assigned the correct roles based on LDAP group membership.
If the redirect URL is misconfigured, sign-in may fail.
Ensure that the redirect URL configured in Microsoft Entra matches the Redirect URL process field in the Login Enterprise.
Break-Glass Access
The local admin account is always available and can be used to sign in even when SSO is enabled and enforced. This account provides break-glass access in case SSO is unavailable or misconfigured.
.png)